Counting of numbers in Hindi is called Hindi Ginti Hindi Sankhya Ginti (हिंदी संख्या गिनती). In this post, you’ll learn to count in Hindi properly.
Hindi numbers can be traced back to Sanskrit. In Hindi, they are called Hindi ginti. The Hindi numerals are used in the Hindi version of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system and are descendants of the Brahmi numerals. The modern Hindi numerals are a combination of two older systems: the Hindi-Arabic (invented by Indian mathematicians) and the Sanskrit numerals. The Hindi- Arabic system is used for most mathematical purposes, but the Sanskrit system is still used in some traditional contexts, such as in certain Vedic rituals.
Table of Content
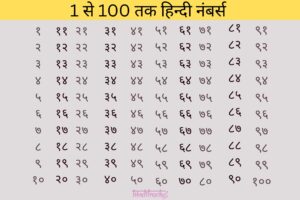
Hindi Numbers 1-100 (Numbers in Hindi)
Hindi Number Counting From 1 to 10 (Hindi Ginti 1 to 10)
| Hindi | English | Number |
|---|---|---|
| शून्य | Shunya (Zero) | ० (0) |
| एक | Ik (One) | १ (1) |
| दो | Do (Two) | २ (2) |
| तीन | Teen (Three) | ३ (3) |
| चार | Chaar (Four) | ४ (4) |
| पाँच | Panch (Five) | ५ (5) |
| छ: | Chhah (Six) | ६ (6) |
| सात | Saat (Seven) | ७ (7) |
| आठ | Aath (Eight) | ८ (8) |
| नौ | Nau (Nine) | ९ (9) |
| दस | Das (Ten) | १० (10) |
Hindi Numbers Counting From 11 to 20 (Hindi Ginti)
| ग्यारह | Gyarah (Eleven) | ११ (11) |
| बारह | Barah (Twelve) | १२ (12) |
| तेरह | Terah (Thirteen) | १३ (13) |
| चौदह | Chaudah (Forteen) | १४ (14) |
| पंद्रह | Pandrah (Fifteen) | १५ (15) |
| सोलह | Solah (Sixteen) | १६ (16) |
| सत्रह | Satrah (Seventeen) | १७ (17) |
| आट्ठारह | Aattharah (Eighteen) | १८ (18) |
| उन्निस | Unnis (Ninteen) | १९ (19) |
| बीस | Bis (Twenty) | २० (20) |
Hindi Numbers Counting From 21 to 30 Numbers in Hindi
| इक्कीस | Ikees (Twenty One) | २१ (21) |
| बाईस | Bayees (Twenty Two) | २२ (22) |
| तेईस | Teyees (Twenty Three) | २३ (23) |
| चौबीस | Chaubees (Twenty Four) | २४ (24) |
| पच्चीस | Pachis (Twenty Five) | २५ (25) |
| छब्बीस | Chhabees (Twenty Six) | २६ (26) |
| सत्ताईस | Sattayes (Twenty Seven) | २७ (27) |
| अट्ठाईस | Attayees (Twenty Eight) | २८ (28) |
| उनतीस | Ynatees (Twenty Nine) | २९ (29) |
| तीस | Tees (Thirty) | ३० (30) |
Hindi Numbers Counting From 31 to 40
| इकत्तीस | Ikatees (Thirty One) | ३१ (31) |
| बत्तीस | Batees (Thirty Two) | ३२ (32) |
| तेंतीस | Tentees (Thirty Three) | ३३ (33) |
| चौंतीस | Chauntees (Thirty Four) | ३४ (34) |
| पैंतीस | Paintees (Thirty Five) | ३५ (35) |
| छत्तीस | Chattis (Thirty Six) | ३६ (36) |
| सैंतीस | Saintees (Thirty Seven) | ३७ (37) |
| अड़तीस | Adatees (Thirty Eight) | ३८ (38) |
| उनतालीस | Unataalees (Thirty Nine) | ३९ (39) |
| चालीस | Chalees (Forty) | ४० (40) |
Hindi Numbers Counting From 41 to 50 Numbers in Hindi
| एकतालीस | Ekatalis (Forty One) | ४१ (41) |
| बायलीस | Bayalis (Forty Two) | ४२ (42) |
| तैंतालीस | Taintalis (Forty Three) | ४३ (43) |
| चौवालीस | Chauwalis (Forty Four) | ४४ (44) |
| पैंतालिस | Paintalis (Forty Five) | ४५ (45) |
| छियालीस | Chhiyalis (Forty Six) | ४६ (46) |
| सैंतालीस | Saintalis (Forty Seven) | ४७ (47) |
| अड़तालीस | Adatalis (Forty Eight) | ४८ (48) |
| उनचास | Unachaas (Forty Nine) | ४९ (49) |
| पचास | Pachaas (Fifty) | ५० (50) |
Hindi Numbers Counting From 51 to 60 Numbers in Hindi
| इक्यबन | Ikyawan (Fifty One) | ५१ (51) |
| बावन | Bawan (Fifty Two) | ५२ (52) |
| तिरपन | Tirpan (Fifty Three) | ५३ (53) |
| चौवन | Chawan (Fifty Four) | ५४ (54) |
| पचपन | Pachpan (Fifty Five) | ५५ (55) |
| छप्पन | Chhappan (Fifty Six) | ५६ (56) |
| सत्तावन | Sattawan (Fifty Seven) | ५७ (57) |
| अट्ठावन | Atthawan (Fifty Eight) | ५८ (58) |
| उनसठ | Unsath (Fifty Nine) | ५९ (59) |
| साठ | Sath (Sixty) | ६० (60) |
Numbers in Hindi From 61 to 70 Numbers in Hindi
| इकसठ | Eksath (Sixty One) | ६१ (61) |
| बासठ | Basath (Sixty Two) | ६२ (62) |
| तिरसठ | Tirsath (Sixty Three) | ६३ (63) |
| चौंसठ | Chausath (Sixty Four) | ६४ (64) |
| पैंसठ | Painsath (Sixty Five) | ६५ (65) |
| छियासठ | Chhiyasath (Sixty Six) | ६६ (66) |
| सड़सठ | Sarsath (Sixty Seven) | ६७ (67) |
| अड़सठ | Arsath (Sixty Eight) | ६८ (68) |
| उनहत्तर | Unahattar (Sixty Nine) | ६९ (69) |
| सत्तर | Sattar (Seventy) | ७० (70) |
Numbers in Hindi From 71 to 80 Numbers in Hindi
| इकहत्तर | Ikahattar (Seventy One) | ७१ (71) |
| बहत्तर | Bahattar (Seventy Two) | ७२ (72) |
| तिहत्तर | Tihattar (Seventy Three) | ७३ (73) |
| चौहत्तर | Chauhattar (Seventy Four) | ७४ (74) |
| पचहत्तर | Pachattar (Seventy Five) | ७५ (75) |
| छीहत्तर | Chihattar (Seventy Six) | ७६ (76) |
| सतहत्तर | Satahattar (Seventy Seven) | ७७ (77) |
| अठहत्तर | Athahattar (Seventy Eight) | ७८ (78) |
| उनासी | Unasi (Seventy Nine) | ७९ (79) |
| अस्सी | Assi (Eighty) | ८० (80) |
Hindi Numbers Counting From 81 to 90 Numbers in Hindi
| इक्यासी | Ikyasi (Eighty One) | ८१ (81) |
| बायसी | Bayasi (Eighty Two) | ८२ (82) |
| तिरासी | Tirasi (Eighty Three) | ८३ (83) |
| चौरासी | Chausasi (Eighty Four) | ८४ (84) |
| पचासी | Pachasi (Eighty Five) | ८५ (85) |
| छियासी | Chhiyasi (Eighty Six) | ८६ (86) |
| सतासी | Satasi (Eighty Seven) | ८७ (87) |
| अट्ठासी | Athasi (Eighty Eight) | ८८ (88) |
| नवासी | Nawasi (Eighty Nine) | ८९ (89) |
| नब्बे | Nabbe (Ninty) | ९० (90) |
Numbers in Hindi From 91 to 100 Numbers in Hindi
| इक्यानवे | Ikyabawe (Eighty One) | ९१ (91) |
| बानवे | Banawe (Eighty Two) | ९२ (92) |
| तिरानवे | Tiranawe (Eighty Three) | ९३ (93) |
| चौरानवे | Chauranawe (Eighty Four) | ९४ (94) |
| पचानवे | Pachanawe (Eighty Five) | ९५ (95) |
| छियानवे | Chhiyanawe (Eighty Six) | ९६ (96) |
| सतानवे | Satanawe (Eighty Seven) | ९७ (97) |
| अट्ठानवे | Atthanawe (Eighty Eight) | ९८ (98) |
| निन्यानवे | Ninyanawe (Eighty Nine) | ९९ (99) |
| सौ | Sau (Hundred) | १०० (100) |
Hindi Numbers 1 to 100
संख्याएँ हमारे जीवन का महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं, और उन्हें जानना बेहद आवश्यक है। हमारे दैनिक जीवन में हम अनगिनत संख्याओं का उपयोग करते हैं, चाहे वह खरीदारी करना हो, समय का पता लगाना हो, या यात्रा करना हो।
हम इस अध्ययन सामग्री के माध्यम से हिंदी में 1 से 100 तक की संख्याओं की गणना करना सिखेंगे। आवश्यकता पड़ने पर, आप इन संख्याओं का उपयोग आसानी से कर पाएंगे। चाहे आप एक बच्चा हों, जो हिंदी संख्याओं को सीख रहा है, या एक वयस्क हों, जो अपने ज्ञान को ताजगी देना चाहता है, यह अध्ययन सामग्री आपके लिए उपयोगी साबित होगी।
More Ways of Counting Numbers in Hindi
| पहला | Pehla (First) | १ला (1st) |
| दूसरा | Dusra (Second) | २रा (2nd) |
| तीसरा | Tisra (Third) | ३रा (3rd) |
| चौथा | Chautha (Forth) | ४था (4th) |
| पाँचवा | Panchwan (Fifth) | ५वाँ (5th) |
| छठा | Chattha (Sixth) | ६ठा (6th) |
| सातवाँ | Saatwan (Seventh) | ७वाँ(7th) |
| आठवाँ | Aathwan (Eighth) | ८वाँ(8th) |
| नौवाँ | Nauwan (Ninth) | ९वाँ (9th) |
| दसवाँ | Daswan (Tenth) | १०वाँ (10th) |
Counting Higher Hindi Numbers
| एक हज़ार | Ik Hazaar (One Thousand) | 1,000 |
| दस हज़ार | Das Hazaar (Ten Thousand) | 10,000 |
| एक लाख | Ik Lakh (Hundred Thousand) | 100,000 |
| दस लाख | Das Lakh (One Million) | 1,000,000 |
| एक करोड़ | Ik Caror (Ten Million) | 10,000,000 |
| दस करोड़ | Das Caror (Hundred Million) | 100,000,000 |
| एक अरब | Ek Arab (One Billion) | 1,000,000,000 |
| एक खरब | Ek Kharab (Hundred Billion) | 100,000,000, 000 |
| नील | Sau Kharab (Ten Trillion) | 10,000,000, 000,000 |
एक पद्मा equal to 100 नील (Nil) or 1 quadrillion.
एक शंख equal to 100 पद्मा (Padma) or 100 quadrillion.
एक महाशंख equal to 100 शंख (Shankh) or 10 quintillion.
Hindi Numbers 1 to 100 Video:
FAQs and Special Hindi Numbers
What is Aadha (आधा) in Hindi ?
Aadha (आधा) is 1/2 (0.5).
What is Paune (पौने) in Hindi ?
Paune (पौने) is 1/4th less in a Number or 15 minutes less in Time.
Example:
For Number: Paune 2 is 1.75; Paune 10 is 9.75
For Time: Paune 2 is 1:45; Paune 10 is 9.45
What is Sawa (सवा) in Hindi ?
Sawa (सवा) is 1/4th more in a Number or 15 minutes more in Time.
Example:
For Number: Sawa 2 is 2.25; Sawa 5 is 5.25
For Time: Sawa 2 is 2:15; Sawa 5 is 5:15
What is Dedh (डेढ़) in Hindi ?
Dedh (डेढ़) is half more than one or Thirty minutes more than one in Time.
Example:
For Number: Dedh is 1.5 (This is a fixed number).
For Time: Dedh is 1:30 (This is a fixed number).
What is Dhai (ढाई) in Hindi ?
Dhai (ढाई) is half more than Two or Thirty minutes more than Two in Time.
Example:
For Number: Dhai is 2.5 (This is a fixed number).
For Time: Dhai is 2:30 (This is a fixed number).
What is Sadhe (साढ़े) in Hindi ?
Sadhe (साढ़े) is half (1/2) more than any number (number must be 3 or more) or Thirty minutes more than any time (time must be 3 or more).
Example:
For Number: Sadhe 3 is 3.5; Sadhe 7 is 7.5
For Time: Sadhe 3 is 3:30; Sadhe 7 is 7:30
What is Paav (पाव) in Hindi ?
Paav (पाव) is 1/4 (0.25) of unit.
Example:
Ek paav Aalu dijiye.
Please give me a quarter kg of potato.
Bonus tips for number learners!!
How many Zeros in US English Counting of Big Numbers?

To count big English numbers, you need to understand this system and the corresponding terms for each power of 10. Here’s a quick reference guide to help you:
10^3: thousand
10^6: million
10^9: billion
10^12: trillion
10^15: quadrillion
10^18: quintillion
10^21: sextillion
10^24: septillion
10^27: octillion
10^30: nonillion
10^33: decillion
10^36: undecillion
10^39: duodecillion
10^42: tredecillion
10^45: quattuordecillion
10^48: quindecillion
10^51: sexdecillion
10^54: septendecillion
10^57: octodecillion
10^60: novemdecillion
10^63: vigintillion




